Ethereum, recognized as the foremost blockchain platform, is celebrated for its robust smart contracts and an extensive ecosystem of decentralized applications (DApps). Yet, its widespread adoption brings forth notable scalability challenges that restrict its interaction with other blockchain platforms. This predicament underscores the importance of Ethereum bridges, which are essential for ensuring seamless asset and data transfers between Ethereum and various blockchain networks.
What Are Ethereum Bridges?

Ethereum bridges refer to specialized protocols crafted to bridge Ethereum with other blockchain environments. These protocols are pivotal in transferring digital assets, data, and functionalities, effectively merging separate blockchain ecosystems. This integration broadens user access to an extensive range of DApps and services beyond the confines of a single blockchain.
Key Varieties of Ethereum Bridges: Ethereum bridges are categorized into two primary types, each serving distinct roles within the blockchain ecosystem:
- Trustless Ethereum Bridges: These bridges leverage smart contracts to autonomously manage and secure asset transfers without intermediaries, embodying the decentralized spirit of blockchain technology.
- Centralized Ethereum Bridges: Relying on intermediaries or third-party validators, these bridges facilitate quicker transactions but at the cost of reduced decentralization.
Both kinds of Ethereum bridges are instrumental in surmounting the scalability and interoperability challenges of the Ethereum network, allowing for smoother interactions across various blockchain ecosystems.
How Ethereum Bridges Operate
The operational mechanism of Ethereum bridges involves locking assets on the source blockchain and minting corresponding tokens on the target blockchain. Here’s an elaboration of this process:
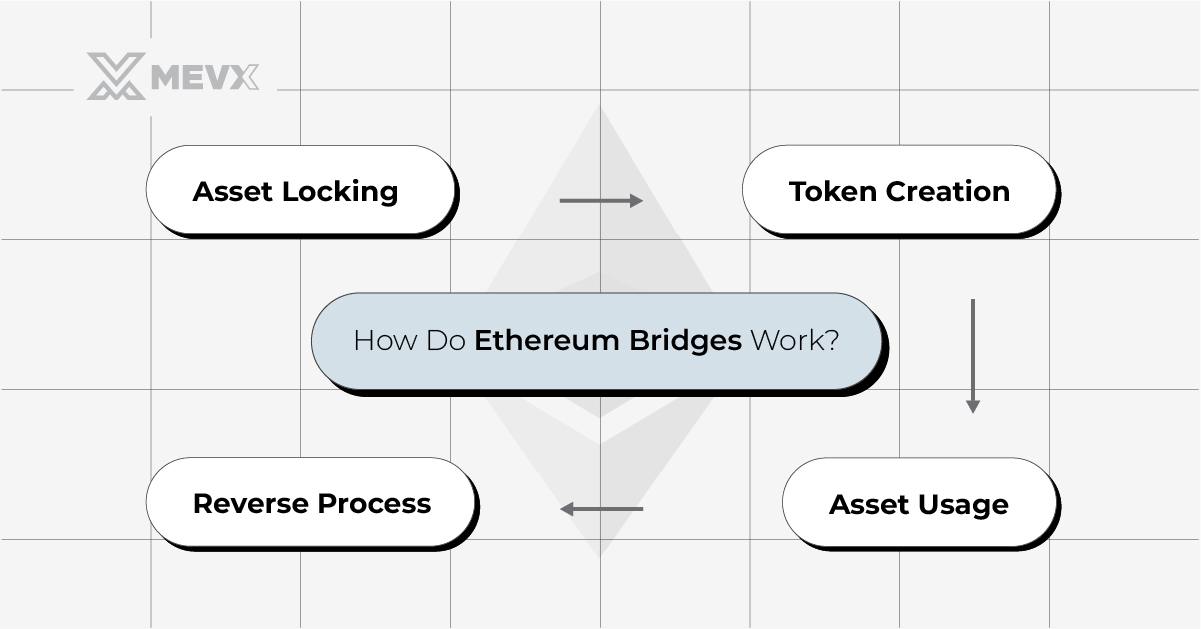
- Asset Locking: Users start by transferring assets to a smart contract on the source blockchain, where these assets are securely locked.
- Token Minting: Corresponding to the locked assets, the bridge protocol mints equivalent tokens on the destination blockchain.
- Asset Utilization: Users can then employ these newly minted tokens within transactions or DApps on the destination blockchain.
- Reverse Mechanism: To retrieve the original assets, the minted tokens on the destination blockchain are destroyed, thereby unlocking the assets on the source blockchain.
This streamlined process significantly enhances the fluidity of asset movement across diverse blockchain platforms.
Advantages of Utilizing Ethereum Bridges
- Enhanced Interoperability: Ethereum bridges extend the functionality of Ethereum DApps to other blockchains, amplifying the ecosystem’s utility.
- Scalability Improvements: These bridges alleviate network congestion by distributing transactions across multiple blockchains, thus reducing Ethereum’s gas fees.
- Increased Liquidity: By facilitating the smooth transfer of assets between networks, bridges enhance market liquidity and enable more diversified investment strategies.
- Innovation Opportunities: By connecting disparate blockchains, Ethereum bridges foster the development of innovative blockchain applications and use cases.
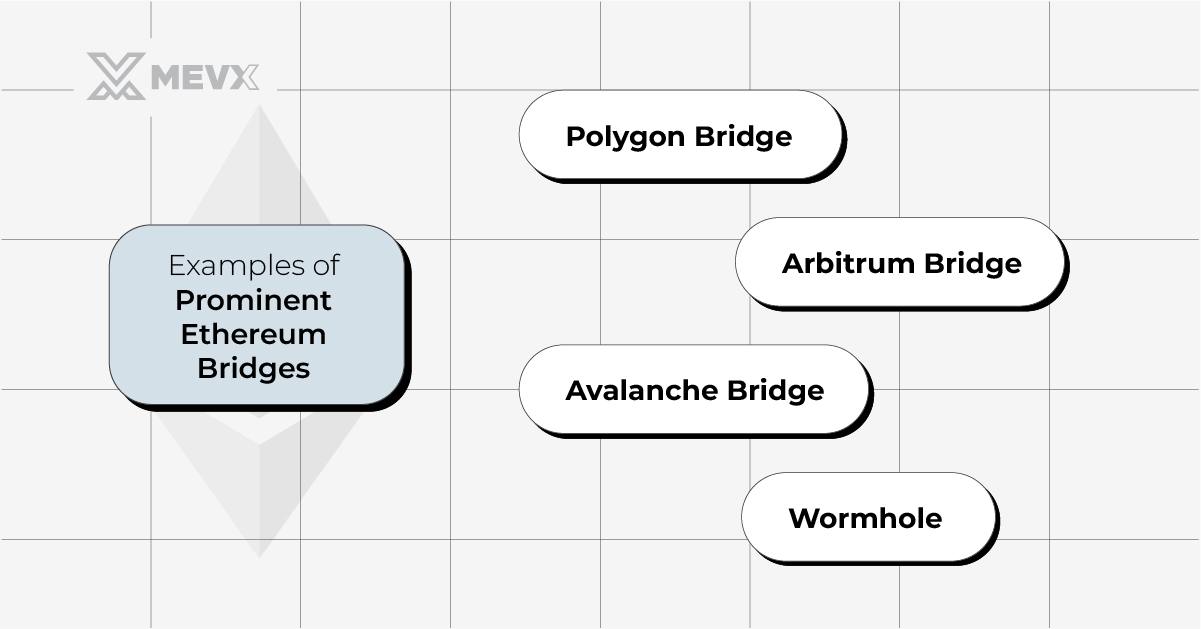
Prominent Examples of Ethereum Bridges
Several Ethereum bridges have gained prominence, offering distinct features and functionalities:
- Polygon Bridge: This Layer-2 solution boosts Ethereum’s scalability, enabling efficient and economical transfers between Ethereum and Polygon networks.
- Arbitrum Bridge: It increases transaction throughput utilizing optimistic roll-ups, ensuring enhanced security.
- Avalanche Bridge: It connects Ethereum with the Avalanche network for fast and cost-effective asset transfers.
- Wormhole: This bridge facilitates the transfer of a variety of token standards, including NFTs, across Ethereum and other leading blockchains such as Solana.
Risks and Challenges Associated with Ethereum Bridges
Despite their benefits, Ethereum bridges are not devoid of risks:
- Vulnerabilities in Smart Contracts: Any exploit in bridge contracts can lead to significant asset losses.
- Centralization Concerns: Centralized bridges introduce potential points of failure and censorship risks.
- Cross-Chain Security Issues: Vulnerabilities in one network can affect assets across connected networks.
Adopting reputable bridges and implementing best security practices are essential to mitigate these risks.
The Significance of Ethereum Bridges
What are Ethereum bridges if not vital tools for promoting interoperability and addressing scalability issues within the blockchain realm? They are indispensable for enabling broader application access and ensuring the blockchain ecosystem’s future, where networks operate in unison, fostering innovation and creativity.
In essence, Ethereum bridges do not merely solve technical challenges; they are catalysts for creating a more interconnected and scalable blockchain environment, set to play an increasingly critical role as blockchain technology advances.
